Week 02 - Shareholder Value Creation
In the second week of lectures, we were given the topic of
International Value Management. Value management is the managing of shareholder
value. The key components of Value Management are Organisational capabilities,
strategy and finance. traditional methods used to measure performance are
Earnings per share and Return on capital employed (ROCE). Earning per share is
calculated by dividing profit, net of tax, dividends to shareholders by the
amount of ordinary shares outstanding. This shows the amount each shareholder
gets if all the net income is distributed among them which usually doesn't happen
and instead they are reinvested in the business. ROCE, on the other hand, means
the profitability ratio of a company it is measured by comparing the
profitability and the capital employed. Moreover, the lecturer briefly explained us about shareholder value creation/destruction, in highly volatile and complicated marketplace, it is important to create shareholder value which can lead to firm's success. The significance of a shareholder is a business concept which is also known as shareholder value maximization or shareholder value model which states that the overall goal of a company is the extent to which it augments shareholders. This theory is used in a number of ways:
- A theory which states that the main goal of the organization is to uphold the wealth of its shareholders mainly by paying a fairly good dividend rate or causing the growth of stock prices
- Market capitalization of the company
Meanwhile, shareholder value shows that a contemporary management philosophy, which states that the organization's success is achieved by inspiring shareholders. A shareholder or a stockholder is an individual who owns a particular asset lawfully in the form of a share of a corporation. Another identification of these particular individuals would be subgroup of stakeholders. They can also be identified as individuals or communities who have interests in the business entity as, suppliers, governments, customers and competitors.
The basic idea of shareholder approach is to increase the value of the organization, cooperation shares and the rate of dividend paid.
The basic idea of shareholder approach is to increase the value of the organization, cooperation shares and the rate of dividend paid.
Shareholder value: (Source: Banerjee, Banerjee Bhabotosh, 1977)
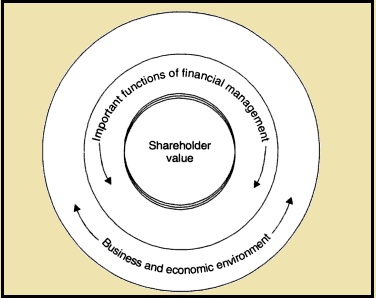
The company cannot determine shareholder value if they do not consider important constituencies. They must be able to uphold a healthy relationship with the customers, employees, government, and suppliers. This idea is basically know as corporate social responsibility operating within an overall framework of shareholder wealth maximization. Furthermore, if effective strategies are not used this could lead to destruction of the shareholders value. According to McKinsey (1996), 80% of the active members destroy the shareholder value. The cause of this is believed to be wrong strategic basis for the deal or of paying too high a price for the target. This error is often called "poor post acquisition implementation". A common example for a similar scenario would be n the merger of Time Warner with AOL and Hewlett-Packard's acquisitions they attempted to double the size of PCs which resulted in a declined PC sales. Here as seen clearly destruction of shareholders has occurred
Further, the lecturer set us an
example of Glencore & Mining industry 2015-2017 case, where the global
industrial metal prices declined rapidly in 2015 which led the company a loss
of $30m of its market value. Therefore, in this case also it is considered as a
shareholder value destruction.
Comments
Post a Comment